Cell mechanics and mechanotransduction by ultrasound and microfludics.
Biomedical ultrasound has evolved into a multi-functional tool for scientific research and medical applications covering imaging, regulation, treatment, etc., and has a wide range of applications in clinical practice. Ultrasound, as a mechanical wave, can stimulate cells and tissues non-invasively and locally with high spatiotemporal precision. It has attracted increasing attention in tissue regeneration, neuromodulation, drug delivery, blood brain barrier opening, and cancer immunotherapy. The mechanical effect of ultrasound on the biological system plays an important role in therapeutic ultrasound, and has began to receive growing attentions.
Research topics
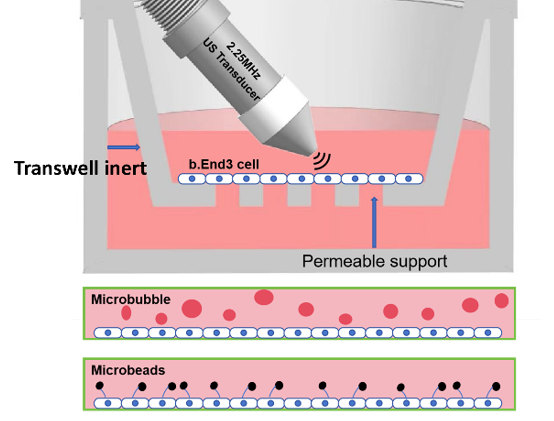
1. Biophysics of cavitation-cell interaction and applicatons: Physics (Cavitation bubble dynamics, jets, acoustic streaming); Bioeffects (cell deformation, sonoporation, calcium signaling, mechanotransduction); Endothelial permeabilization (BBB opening, tight junction regulation, paracellular transport), Sonodynamics.
Cavitation-cell interaction; Vascular drug delivery


2. Ultrasound neuromodulation: mechanisms (electrophysiology and 2-photon imaging); therapeutic applications (brain disease intervention); new techniques development (sonogenetics, ultrasound devices, brain-machine interface)